Users
13,00,000
Users from 2600 towns trust TaxBuddy
Impact
94%
That’s how many 1st time users save tax with TaxBuddy
Founded
2017
Led by a team of ex-IRS joint commissioners and accomplished CAs We are India's highest rated and most trusted assisted tax filing platform.
India’s First AI-powered Platform for ITR Filing and Tax Compliance
Experience fast, reliable, and secure online ITR filing with TaxBuddy.
Free notice management with expert-backed e-tax filing support
Year-round query resolution with India’s top assisted ITR filing platform
Trusted by startups, salaried professionals & freelancers
TaxBuddy: Your AI-Driven Partner for Online Income Tax Filing
We simplify your e-filing journey with powerful automation and human expertise.
Taxbuddy is your ideal partner for assisted Income Tax Filing as we offer

Expert-Assisted Income Tax eFiling Services
Get personalized help from our in-house professionals. Whether you're filing as a salaried employee, freelancer, or managing a business, our team ensures 100% accuracy and maximum savings—backed by one of India’s most trusted online e-tax filing platforms.

Secure Online ITR Filing Platform
Your data is safe with us. TaxBuddy’s secure e-tax filing services use advanced encryption to keep your personal and financial information private.

Timely, Hassle-Free ITR Filing
Stay ahead of deadlines with AI-powered reminders and automated updates. Our system ensures smooth, compliant Income Tax Return Filing — always on time.

Seamless Filing with Smart Tools
Upload Form 16, review Form 26AS, and auto-import income details using our integrated income tax filing tool. Our online incometax filing services cover everything from salary to capital gains and house property.
Take Control of Your Taxes
Join lakhs of Indians using TaxBuddy—India’s most secure and easy-to-use income tax e-filing website for individuals and businesses.
Crores Saved Through Smart, AI-Driven ITR Filing
Simplifying Income Tax e-Filing for Every Indian
At TaxBuddy, we combine intelligent automation with expert assistance to make income tax e filing simple, secure, and stress-free. Our assisted ITR filing platform helps salaried individuals, professionals, and startups file returns accurately, claim every deduction, and stay compliant — all on India’s most trusted secure online ITR filing platform.
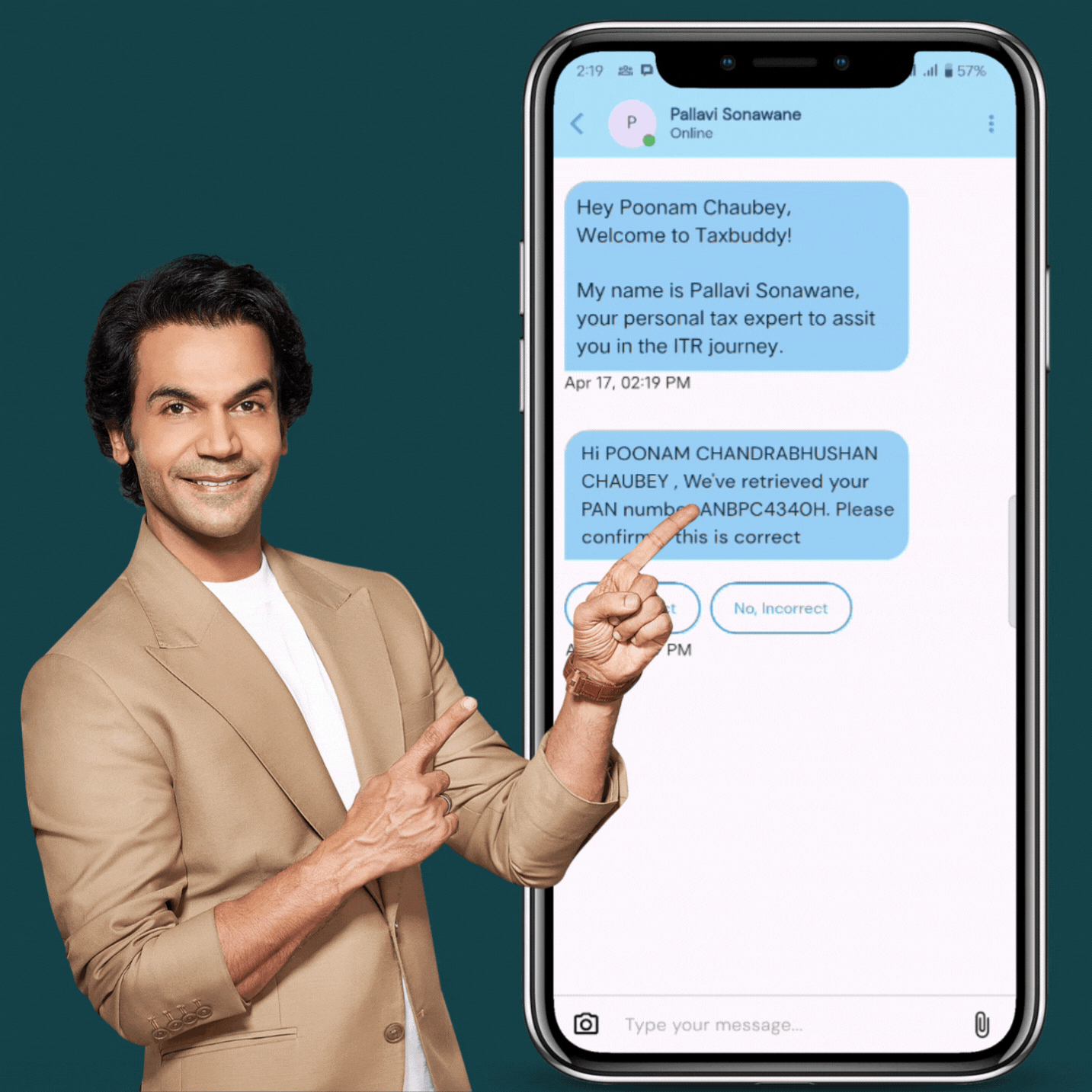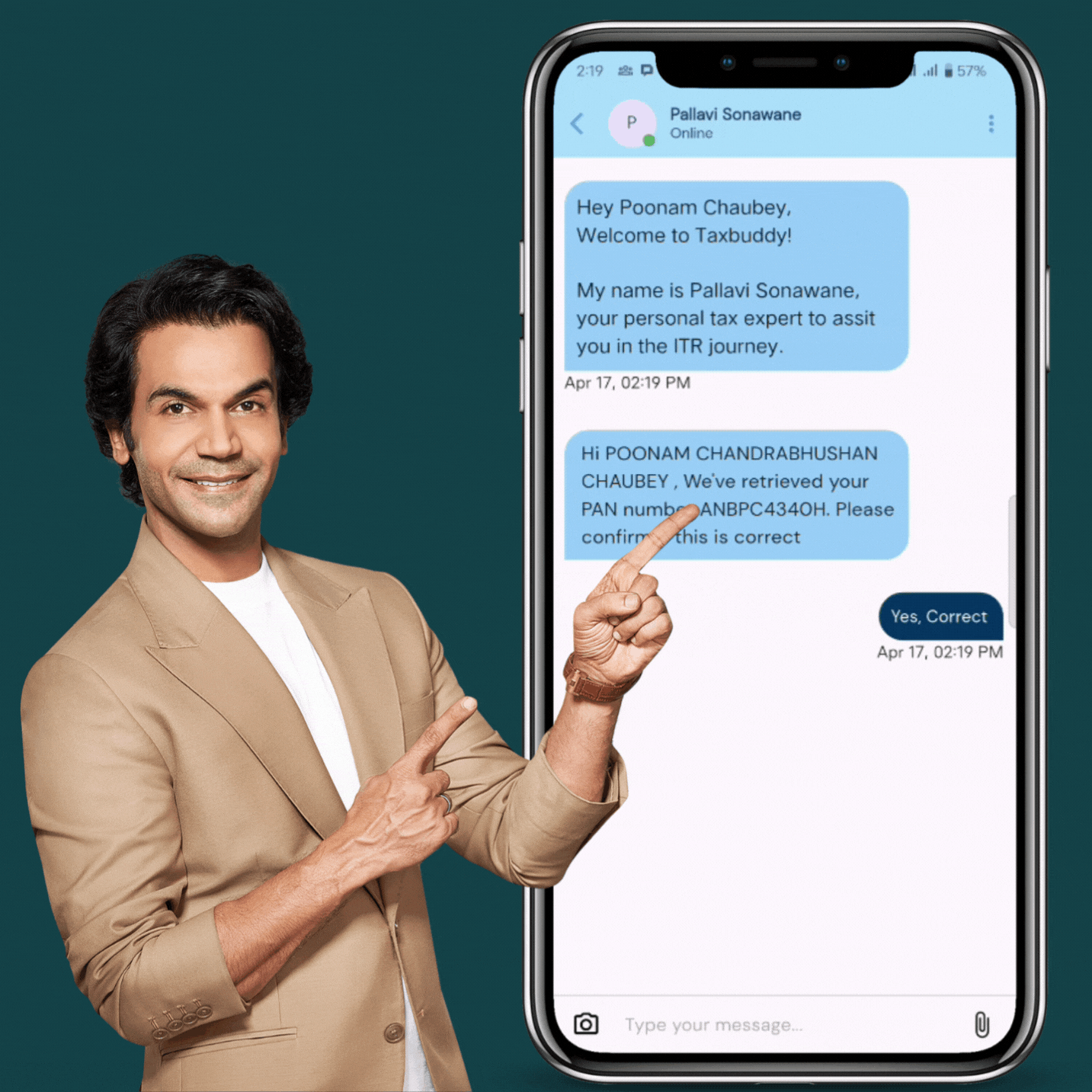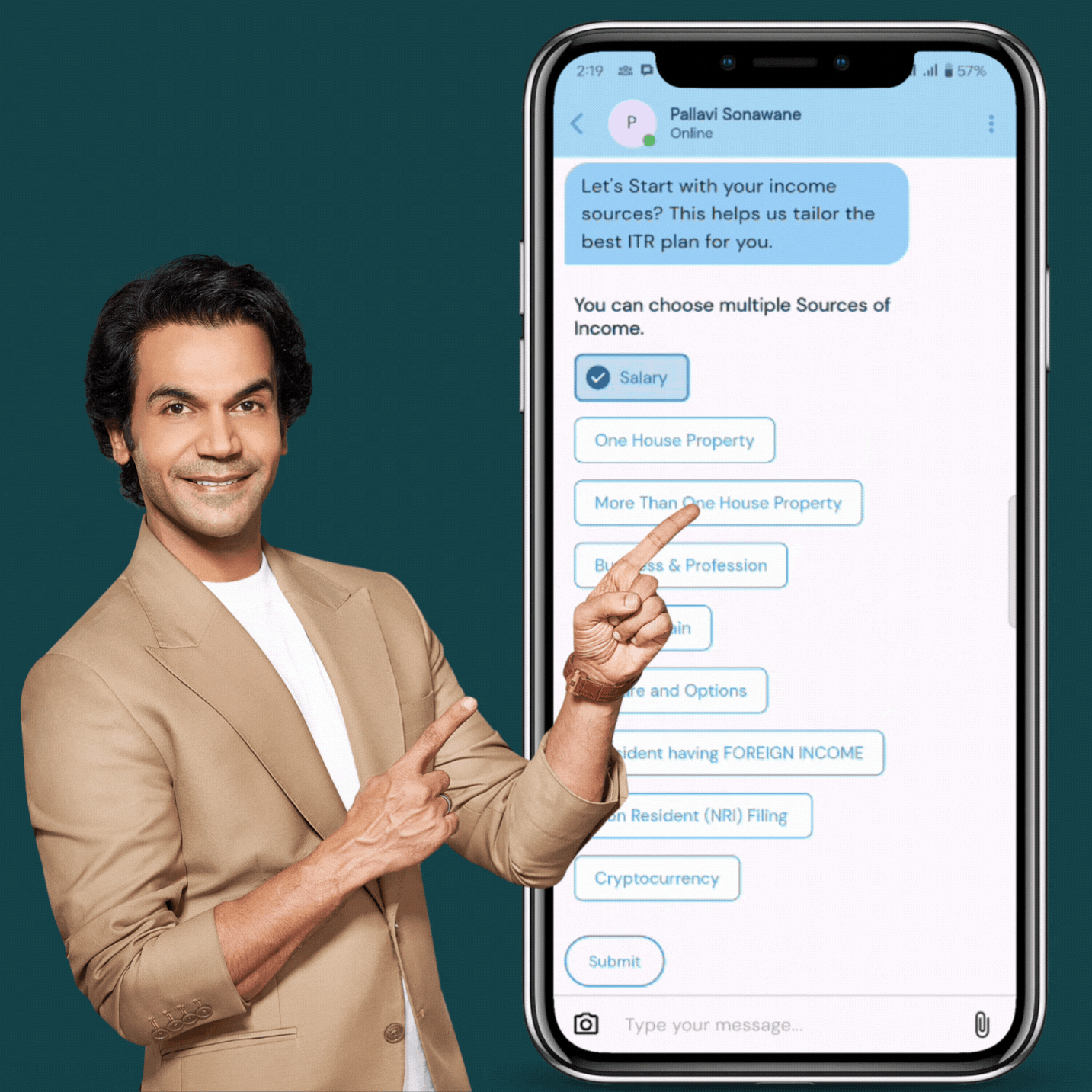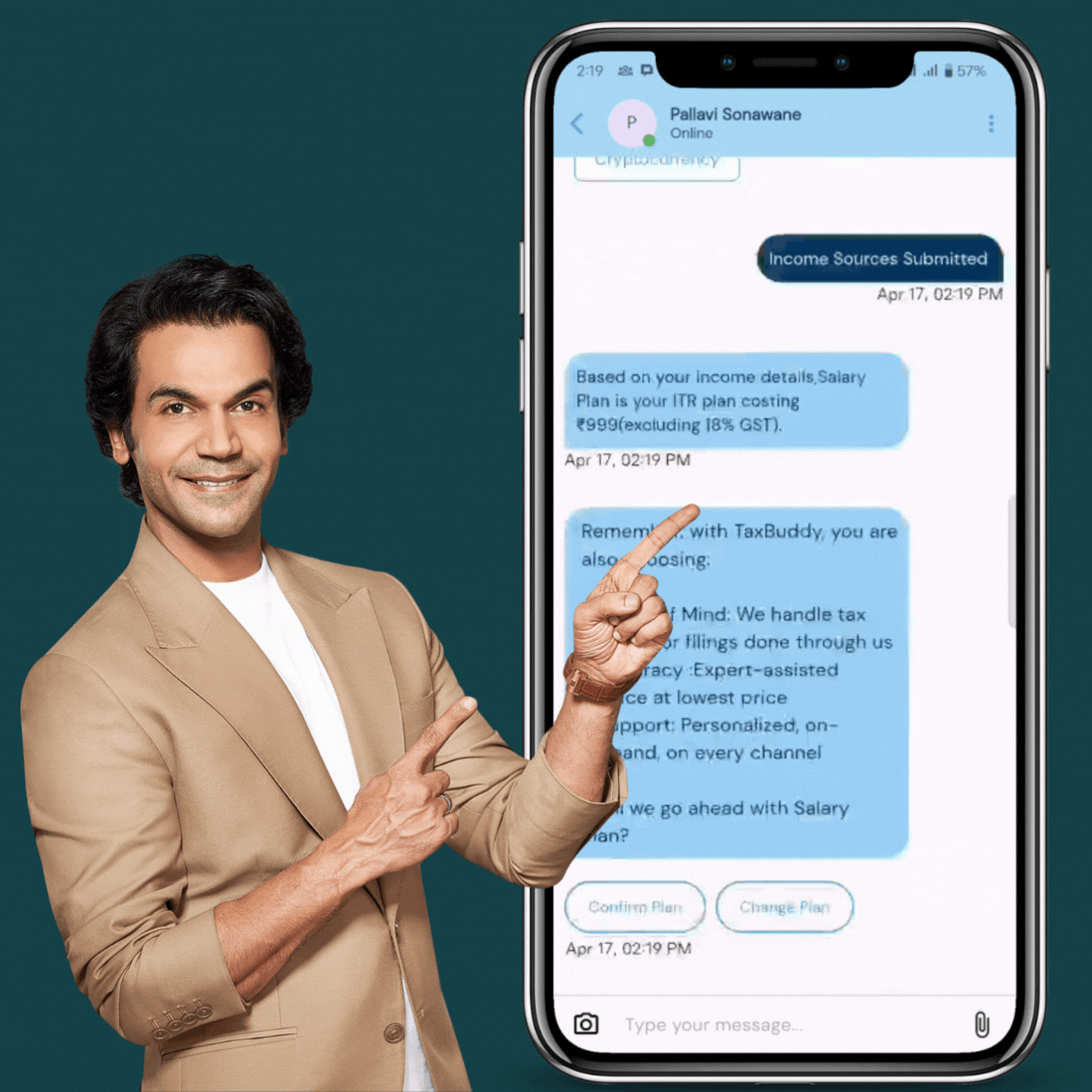
How Assisted ITR Filing Works with TaxBuddy
1
2
3
4
Connect Instantly via Live Chat
Get expert support through our online income tax filing service, available right from your browser or mobile.
Share Your Tax Details Securely
Upload Form 16, TDS details, and investment proofs via our encrypted, secure e-tax filing service.
Review, Approve & File
We prepare your return, summarize it for your approval, and ensure 100% accurate income tax return filing.
Get ITR Filed in 24 Hour
Enjoy lightning-fast turnaround. Your ITR is filed online, error-free, and within 24 hours—guaranteed.
Real Experts. Real Support. True Assisted Tax Compliance.
No Hidden Charges — Ever
Enjoy complete peace of mind with fully transparent pricing. Our income tax filing services are designed to be secure, reliable, and always backed by expert support.
✅ 97.4% Users Get It Right the First Time
With our expert-assisted ITR filing, most users file error-free on the first attempt. Got a tax notice? No worries — our team handles it at no extra cost through our secure online ITR filing platform.

Need More Than Just Filing? TaxBuddy’s Got You Covered
Smart Services for Individuals
Personalized ITR Filing Support
Whether you’re a salaried employee, NRI, freelancer, or capital gains investor — our expert-assisted ITR filing ensures accurate, AI-backed e-filing tailored to your tax situation.
TDS on Property Sale (Form 26QB)
Selling real estate? We handle your TDS compliance under Section 194-IA and file Form 26QB correctly through our secure e-tax filing services — no hassle, no delay.
Legal Review for Personal Finance
Need HRA validation, rent agreement help, or investment proof prep? Our team ensures your documents meet tax standards for seamless income tax e filing.
Complete Compliance Suite for Startups & Small Businesses
End-to-End Tax Filing for Businesses
From GST returns to ITR, our income tax filing services cover all compliance needs so you can focus on scaling while we handle the filings.
Business Registrations Made Easy
Get expert guidance on PF, ESI, PAN, Shop Act, and FSSAI registrations — all supported by TaxBuddy’s trusted online incometax filing services for entrepreneurs.
Trademarks & DSC Assistance
Secure your brand identity and compliance with our quick help for trademark registration, renewal, and Digital Signature Certificates (DSC) setup — fully compliant and startup-ready.
TaxBuddy Portfolio Doctor
Get Your Investment Portfolio Analyzed in Minutes
Upload your CAS report and let our AI-driven engine analyze your current holdings. Instantly discover top performers, laggards, and personalized insights to optimize your investments for better tax efficiency.


TaxBuddy Wealth Builder
Assisted Investment Planning Backed by Tax Insight
Get expert-assisted, actionable advice customized to your income, tax profile, and future goals. Whether you’re salaried, self-employed, or an NRI, our secure online platform helps align your investments with smarter tax planning strategies.
Invest in ‘Zero-Commission’ Mutual Funds
Compare Funds. Understand Risk. Invest Smarter.
Use our advanced rating system to evaluate top-performing mutual funds. Track historical returns, assess risk levels, and project future performance — all within a secure, intuitive dashboard.

What Our Clients Say About TaxBuddy

Niranjana Sharma
Local Guide • 2 months ago
Team TaxBuddy came to the rescue in crunch time. They were prompt, courteous and professional. Superlative service a super competitive price. Couldn't be more satisfied. Strongly recommended for every taxpayer in India who wants accurate returns and peace of mind.
Google Reviews
4.7
Rohan Baruah
3 months ago
Positive : Professionalism, Responsiveness. Rajkumar was very responsive and prompt throughout the return filing process. Even though it was taking some time on the govt portal, I knew that the work
Google Reviews
5.0
Rahul Patil
Local Guide • 2 months ago
Positive : Quality.
Right from the start the process was very smooth. The tax buddy assigned (Mr Gaurishankar) was extremely helpful, proactive, patient and answered all questions. Not only did I avail the service, because of the great experience, made my spouse use the service as well...
Google Reviews
4.7
R
Subham Saurabh
1 month ago
TaxBuddy was a breeze to work with. It's a straightforward procedure that's easy to follow. All you have to do is fill out the form with the relevant information and submit necessary documents as requested by them.
Google Reviews
4.9
.png)
Aahan Shetty
1 month ago
TaxBuddy has been a real buddy for me throughout my e-filing process. As a high-income professional, I have always struggled with high tax bills and refund concerns. Thankfully, now I have a partner I can trust to guide me for maximum savings.
Google Reviews
5.0

ET Now Best Brands 2024

Frequently asked questions
Q
What is the revised last date for ITR filing for FY 2024–25 (AY 2025-26)?
A
The Income Tax Department has extended the ITR filing due date for FY 2024–25 (AY 2025–26) to September 16, 2025, for individuals not subject to audit. Filing before the deadline ensures timely refunds, avoids late fees, and keeps your tax records clean. You can complete your return anytime using TaxBuddy’s secure online income tax filing services.
Q
What is Tax Filing?
A
Tax filing is the process of submitting your income and tax details to the Income Tax Department through an official income tax return (ITR). It ensures compliance, transparency, and enables the government to assess whether you’ve paid the right amount of tax. If you’ve paid more tax than required, you’re eligible for a refund. Platforms like TaxBuddy offer a reliable online income tax filing service to simplify this process for individuals and businesses alike.
Q
Who is required to file an ITR for FY 2024–25?
A
Anyone with an annual income exceeding ₹2.5 lakh must file an ITR. For senior citizens (60–79 years), the limit is ₹3 lakh, and for super senior citizens (80+), it’s ₹5 lakh. Additionally, individuals earning capital gains, interest income, rental income, or foreign income are also required to file. Filing through a secure online ITR filing platform like TaxBuddy helps meet your compliance requirements with ease.
Q
What are the benefits of E-Tax Filing with TaxBuddy?
A
E-tax filing with TaxBuddy is designed to simplify your tax experience while ensuring accuracy, security, and expert support. Whether you're a salaried individual, NRI, freelancer, or a business owner, our online income tax filing service adapts to your unique needs.
Here’s how you benefit:
-
Quick and accurate filing: Our AI-driven income tax filing tool auto-fills your return using documents like Form 16 and matches data from Form 26AS and AIS to reduce errors.
-
Expert-assisted support: Prefer guidance? Our professionals review your return, help optimize deductions, and ensure full compliance.
-
Anytime, anywhere access: Use our secure online ITR filing platform to file from home, office, or on the go — no physical visits required.
-
Data privacy and security: Your information is protected through 256-bit encryption and hosted on secure servers.
-
Post-filing assistance: We provide free notice management and year-round support, even after you’ve filed your ITR.
-
Support for all income types: From salary and capital gains to rental income and freelance work, our platform handles it all — including tax filing services for startups.
TaxBuddy is more than just an e-filing website — it’s a secure, reliable partner for all your income tax compliance needs.
Q
I receive a salary after TDS deduction. Do I still need to file an ITR?
Q
How do I claim a tax refund?
A
If excess tax has been paid via TDS or advance tax, a refund can be claimed by filing your return through TaxBuddy. Our secure online ITR filing platform calculates your eligible refund based on actual tax liability. Once filed and e-verified, the refund is processed by the department and credited directly to your bank account.
Q
How do I check my Form 26AS and TDS details?
Q
What are the latest ITR changes for FY 2024–25 (AY 2025-26)?
A
Here are key updates for the current assessment year:
-
ITR-1 and ITR-4 can now be used by individuals with LTCG up to ₹1.25 lakh.
-
Aadhaar Enrolment ID is no longer accepted — only Aadhaar number.
-
ITR-4 now asks for declaration if you're opting out of the new regime.
-
More clarity in reporting exempt income and income from foreign sources.
TaxBuddy keeps its online ITR filing tool updated in real-time to reflect these changes.
Q
What is the default tax regime and can I opt out?
Q
How do I e-verify my ITR after submission?
Q
Can I revise my ITR if I made a mistake?
Q
What if I receive a tax notice?
A
TaxBuddy provides year-round support to help you respond to tax notices. Whether it's a mismatch notice (Section 143(1)), refund adjustment (Section 245), or defective return (Section 139(9)), our tax professionals help resolve it promptly. Our secure e-tax filing services include free notice management for returns filed through us.
Q
Can TaxBuddy help startups and small businesses with tax filing?
Q
What documents do I need to file my Income Tax Return online?
Q
How soon can I expect my tax refund after filing through TaxBuddy?
Q
Can I file income tax returns for multiple assessment years on TaxBuddy?
Q
What is the difference between e-filing and manual filing of ITR?
Q
Does TaxBuddy provide assistance for income from capital gains and property rental?
Q
How do I know if I am eligible for the presumptive taxation scheme?
Q
Can I file income tax returns offline and upload them later on TaxBuddy?